SOLVENT VS. NON-SOLVENT INKS
What's the difference and which should you use?
When it comes to printing — especially for signage, tarpaulins, or outdoor materials — you’ve probably heard the terms “solvent ink” and “non-solvent ink.” But what do they actually mean, and why does it matter which one you use?
Let’s break it down clearly and simply in this guide, comparing their chemistry, performance, pros and cons, and best applications.
Table of Contents
What Are Solvent Inks?
Solvent inks use organic chemical solvents as the liquid base that carries color pigments. These solvents dissolve the pigment and help the ink penetrate or adhere to non-porous materials such as PVC, vinyl, or tarpaulin.
When printed, the solvent evaporates, leaving the pigment firmly attached to the surface — creating a waterproof and UV-resistant image ideal for outdoor use.
💡 Common Uses:
- Outdoor banners and tarpaulins
- Vehicle wraps and stickers
- Billboards and Signages
- Long-term outdoor graphics
✅ Advantages:
- Excellent adhesion to PVC and vinyl surfaces
- Waterproof and weather-resistant — perfect for outdoor applications
- Vivid, durable colors that resist fading for months or years
- Flexible prints that can be rolled, stretched, or folded
⚠️ Disadvantages:
- Strong odor (contains VOCs — volatile organic compounds)
- Requires proper ventilation and careful handling
- May damage certain coated papers or fabrics
- Not eco-friendly due to chemical solvents
What Are Non-Solvent Inks?
“Non-solvent inks” is a broad category that includes inks that don’t rely on strong chemical solvents. Instead, they use water, UV-curable resins, or latex polymers as carriers.
These inks are more environmentally friendly, have less odor, and are safer to use indoors — but they differ in how they adhere and cure.
🌱 Types of Non-Solvent Inks:
- Aqueous (Water-based) — Uses water as a carrier; best for coated papers, posters, and indoor prints.
- Latex — A water-based ink with heat-activated polymers that form a flexible, durable film.
- UV-Curable — Uses liquid resin cured by UV light to harden instantly on the surface.
✅ Advantages:
- Low odor and environmentally friendly (fewer or no VOCs)
- Safer for indoor use — offices, malls, and enclosed spaces
- Excellent color quality for coated materials
- Instant curing for UV inks — no drying time needed
⚠️ Disadvantages:
- Less adhesion on uncoated PVC unless specially treated
- Less flexible for some UV inks (may crack when folded)
- Higher printer cost (especially UV and latex systems)
Water-based inks are not fully waterproof unless laminated or coated media is used
Side-by-Side Comparison
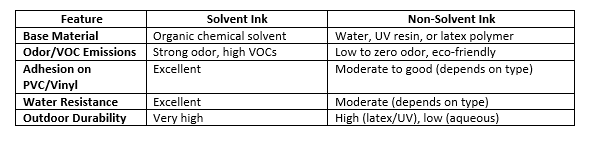
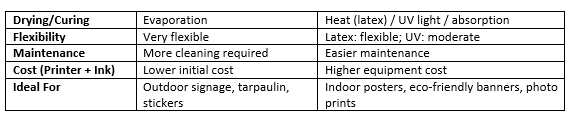
When to Use Each Ink Type
🧱 Use Solvent Ink If:
- You’re printing tarpaulins, outdoor billboards, or vehicle wraps
- You need long-lasting, weather-resistant prints
- You have a well-ventilated printing area
- You want strong adhesion on PVC or vinyl materials
🏠 Use Non-Solvent Ink If:
- You’re printing indoor displays, posters, or wall graphics
- You need low-odor, eco-friendly printing (e.g., for malls or schools)
- You prioritize safety and environmental compliance
- You print on coated papers, textiles, or specialty substrates
Conclusion
Choosing between solvent and non-solvent ink comes down to where your prints will be used and what they’ll be printed on.
- For outdoor, long-term, and waterproof needs — go with solvent or eco-solvent ink.
- For indoor, eco-friendly, and low-odor printing — go with non-solvent ink like latex or UV.
Each ink has its own strengths: solvent inks dominate outdoor durability, while non-solvent inks lead in safety, sustainability, and indoor use.

